The rising demand for more space-efficient laboratory technology combined with laboratory process innovation is challenging motion control application designers to deliver small-scale systems without compromising performance. Luckily, select motion control component manufacturers are helping meet this demand by offering standard parts in smaller sizes, hybrid assemblies that eliminate the need for certain components and extensive customization capabilities.
Scaling down
Laboratory instruments are getting smaller. Analytical instruments that once required a room of their own now sit on the benchtop. The trend toward miniaturization is especially welcome among laboratory managers and diagnosticians seeking to make the most cost-efficient use of floor and benchtop space. It also fast-tracks testing by eliminating the need to send samples out to a lab and wait for results.
Complementing the miniaturization trend are space-efficient process innovations such as cartridges that enable multiple reagent tests at a single point; a high density of well plates that can handle multiple assays and specialized instruments dedicated to small batch assays.
Much of the move toward miniaturization and process efficiency involves automation, which challenges motion control system designers to scale these systems down while achieving the same or better performance.
Sourcing options
Designers developing motion control systems to fit into smaller spaces have three primary options: they can use smaller components, those that do not require external support, or work with manufacturers to develop custom solutions.
Designing with Smaller Components
Once a designer knows how much space they have to work with, they are better equipped to meet customer requirements with standard components. The miniaturization of laboratory systems has been going on for at least 10 years, during which time increased demand has resulted in wider market availability of smaller components, including size 8 stepper motors and 3 mm Ball Bushing® bearings.
Blood diagnostic and treatment systems, for example, are getting smaller and smaller. An equipment designer was redesigning a large standalone blood-cleansing device to fit on a desktop. The system used UV light to kill pathogens and required motion control to keep the sample constantly agitated for maximum UV exposure. Reducing the width was the primary need. They accomplished this with miniature profile rail assemblies, which enabled them to reduce the height as well. The designer also specified motorized lead screws, which could be tucked behind other components rather than extending outward in any direction, enabling an even more compact design.
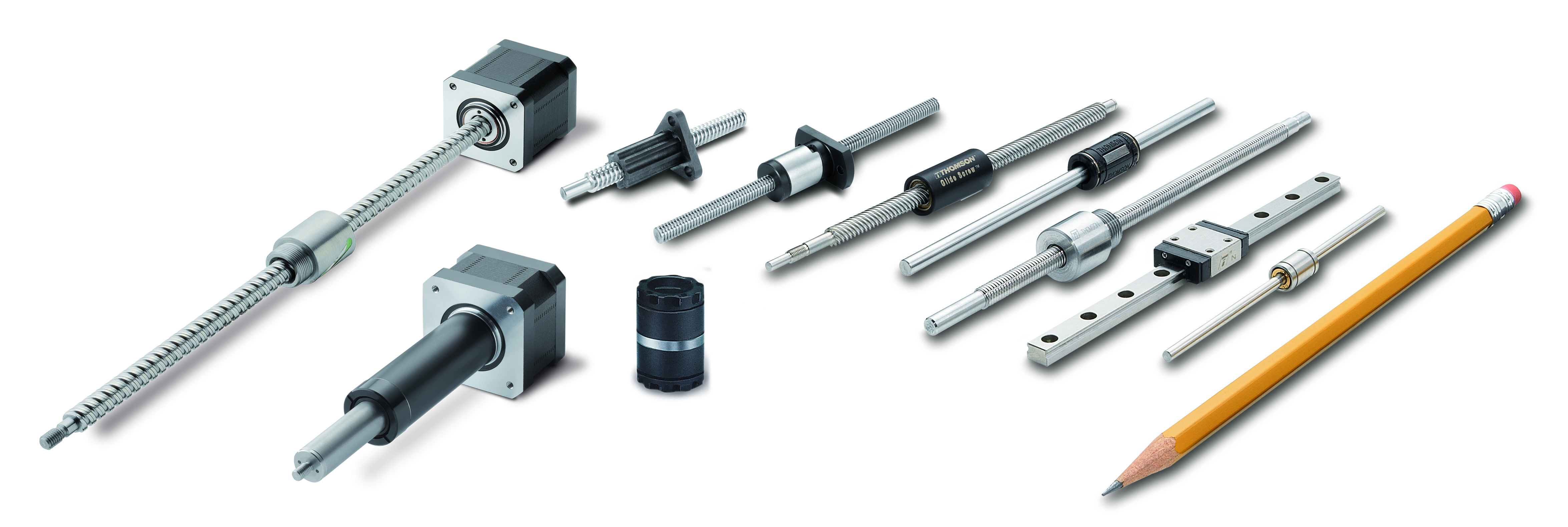

Miniature linear motion components can help designers meet even the most stringent space requirements for today’s medical equipment.
Miniaturized innovations such as these are also being applied to “point-of-care” diagnostics, which would bring blood test results right to the doctor’s office or even portable devices that could be used in the home. With smaller-scale testing instruments, lab diagnostics could be available in a matter of minutes instead of days. This level of improved speed and accessibility of testing has the potential to save countless lives.
Eliminating the need for external linear support
For space-constrained, force-sensitive applications requiring shorter strokes that must be repeated with high precision, such as vertically positioning a pipette over a test tube array, designers can economize space using a motorized lead screw actuator (MLA). Doing so with conventional basic stepper motor and lead screw assemblies would require designing costly external linear guidance systems for anti-rotation of the nut, and guidance of the system. The hybrid approach, however, eliminates the need for external linear guidance by surrounding the shaft with an aluminum cover tube with molded internal splines that lock onto the nut to keep it from turning and provide linear guidance.
Eliminating the need for an external guidance component gives the designer more flexibility to reduce the size of the axis, which helps reduce the overall footprint of the instrument.
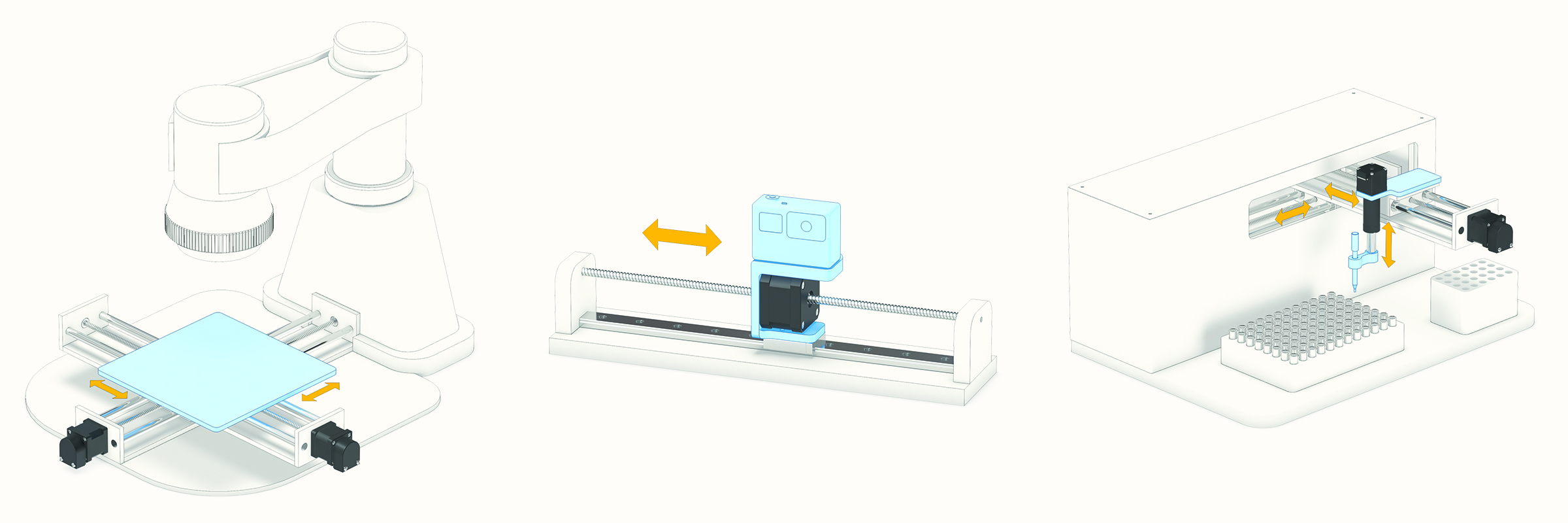
By reducing the total number of components needed, stepper motor linear actuators are ideal for reducing the size of the axis on a wide variety of space-conscious applications, including (left to right): XY stage (rotating screws), horizontal positioning (rotating nut), and fluid pipetting (telescoping and rotating screw).
Customization
If a designer cannot get the motion they need with standard components, they will have to work with manufacturers to create custom solutions. In most cases, however, the customization process does not involve starting from scratch but modifying existing standard components to overcome limitations. Ball nuts, for example, are often designed for use with screws of different diameters. This design choice reduces the cost but does require a slightly larger nut. To save space on an application using a smaller diameter screw, a smaller nut could be developed.
Sometimes, it is just a matter of modifying the mounting. For example, when working on a new spectrophotometer to highly analyze color samples on the desktop, a designer needed linear motion components to be as compact as possible. They selected a single miniature profile rail assembly to guide the lenses of the spectrophotometer into position. The miniature rail enabled not only a compact profile but also a high load capacity and whisper-quiet movement. Along with compactness, however, high rigidity was critical in this application. Achieving that required attaching the miniature profile rail to another component within the machine instead of a separate mounting surface. This feat required a customized counterbore of the standard mounting holes of the profile rail assembly.
Another factor to consider in customization is the supply chain. Whether it be sub-components, plating, materials, engineering services or other contributors, manufacturers often depend upon external part sources. These must also be evaluated based on whether their standard products are suitable for smaller-scale designs.
Smaller technology; bigger difference
Market demand for immediacy, space constraints and pandemic-induced health concerns will likely continue to drive the need for increasingly smaller medical equipment. Motion control components can make up a substantial portion of medical machinery footprint, and manufacturers are actively innovating to deliver full functionality in smaller spaces. The likely result is lower healthcare costs and better outcomes for patients.